How to Create an NFT
Author: Alchemy Team
This tutorial will walk you through writing and deploying a Non Fungible (ERC721) Token smart contract using Ethereum and Inter Planetary File System (IPFS).
Estimated time to complete this guide: ~15 minutes
Even if you've been living under a rock, you'll have noticed that every major news outlet has been profiling the rise of NFTs.
With NFTs bringing blockchain into the public eye, now is an excellent opportunity to understand the hype yourself by publishing your own NFT (ERC-721 Token) on the Ethereum blockchain!
In this tutorial, we will walk through creating and deploying an ERC-721 smart contract on the Ropsten test network using Metamask, Solidity, Hardhat, Pinata and Alchemy (don’t fret if you don’t understand what any of this means yet— we will explain it). In Part II of this tutorial, we’ll go through how we can use our smart contract to mint an NFT, and in Part III we’ll cover how to view your NFT on Metamask.
And of course, if you have questions at any point, don't hesitate to reach out in the Alchemy Discord!
Step 1: Connect to the Ethereum network
There a bunch of ways to make requests to the Ethereum blockchain, but to make things easiest, we’ll use a free account on Alchemy, a blockchain developer platform and API that allows us to communicate with the Ethereum chain without having to run our own nodes.
In this tutorial, we'll also take advantage of Alchemy's developer tools for monitoring and analytics to understand what’s going on under the hood in our smart contract deployment. If you don’t already have an Alchemy account, you can sign up for free here.
Step 2: Create your app (and API key)
Once you’ve created an Alchemy account, you can generate an API key by creating an app. This will allow us to make requests to the Ropsten test network. Check out this guide if you're curious to learn more about test networks.
Navigate to the “Create App” page in your Alchemy Dashboard by hovering over “Apps” in the nav bar and clicking “Create App”
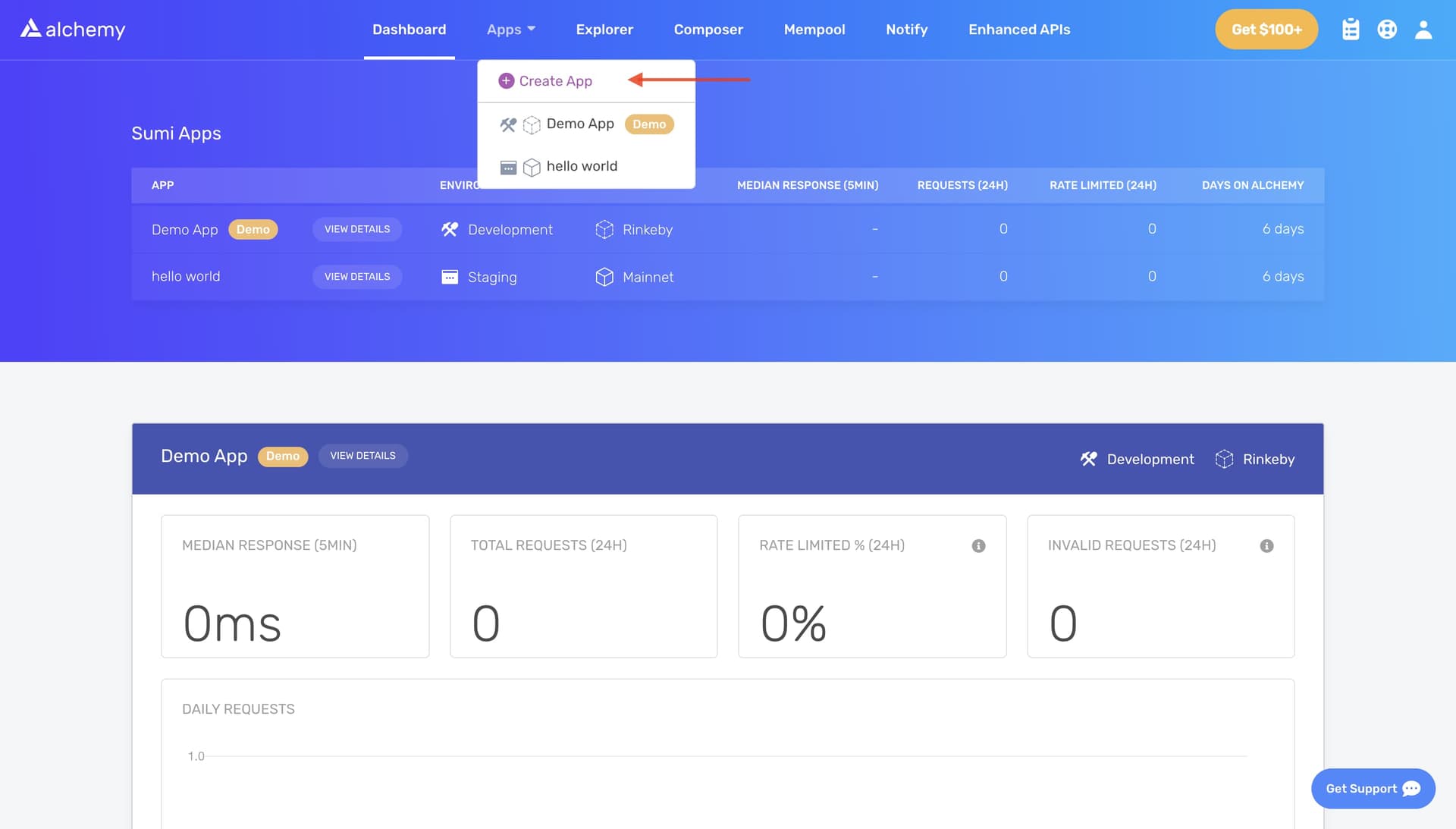
2. Name your app (we chose "My First NFT!"), offer a short description, select “Staging” for the Environment (used for your app bookkeeping), and choose “Ropsten” for your network.
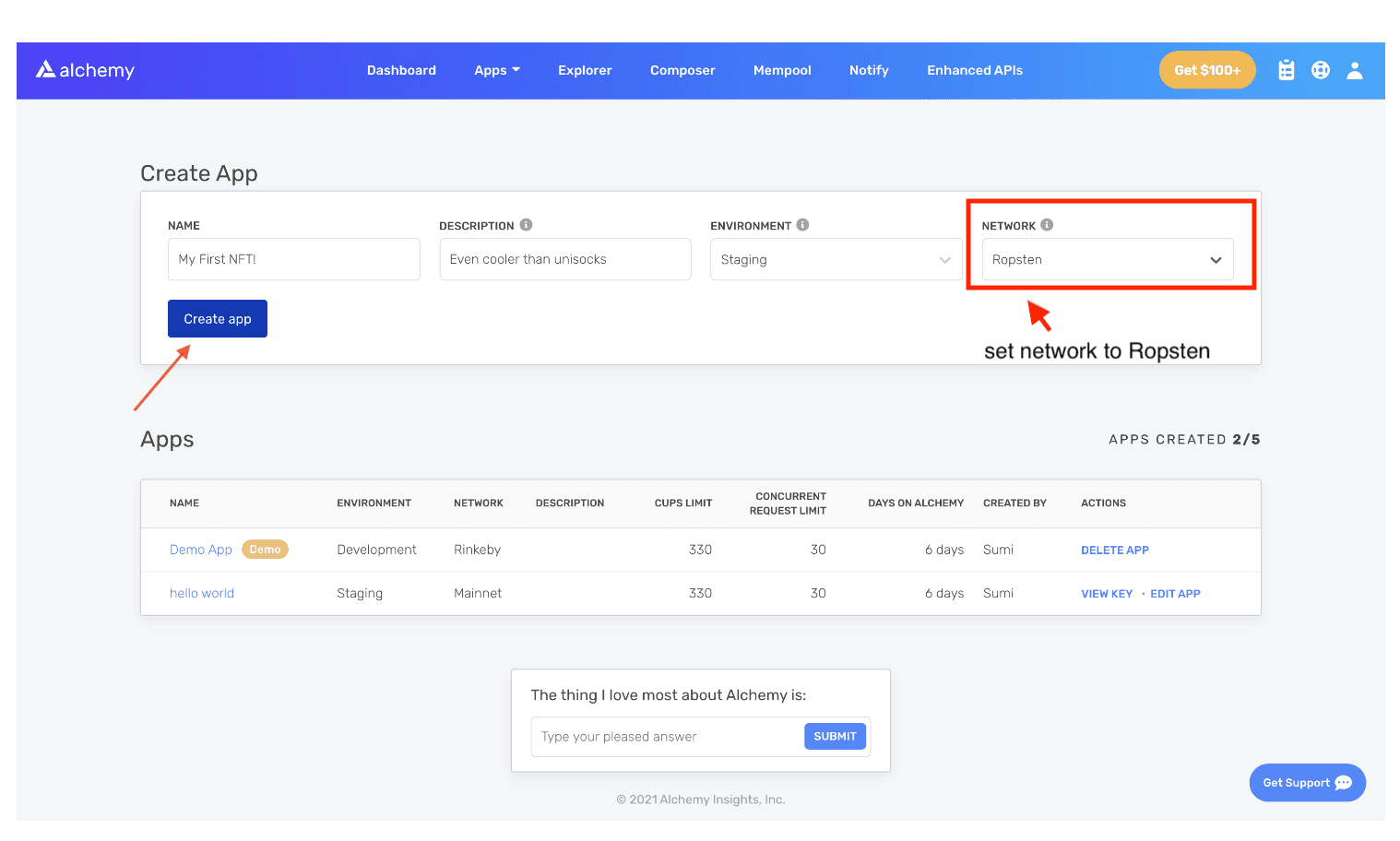
3. Click “Create app” and that’s it! Your app should appear in the table below.
Step 3: Create an Ethereum account (address)
We need an Ethereum account to send and receive transactions. For this tutorial, we’ll use Metamask, a virtual wallet in the browser used to manage your Ethereum account address. If you want to understand more about how transactions on Ethereum work, check out this page from the Ethereum foundation.
You can download and create a Metamask account for free here. When you are creating an account, or if you already have an account, make sure to switch over to the “Ropsten Test Network” in the upper right (so that we’re not dealing with real money).
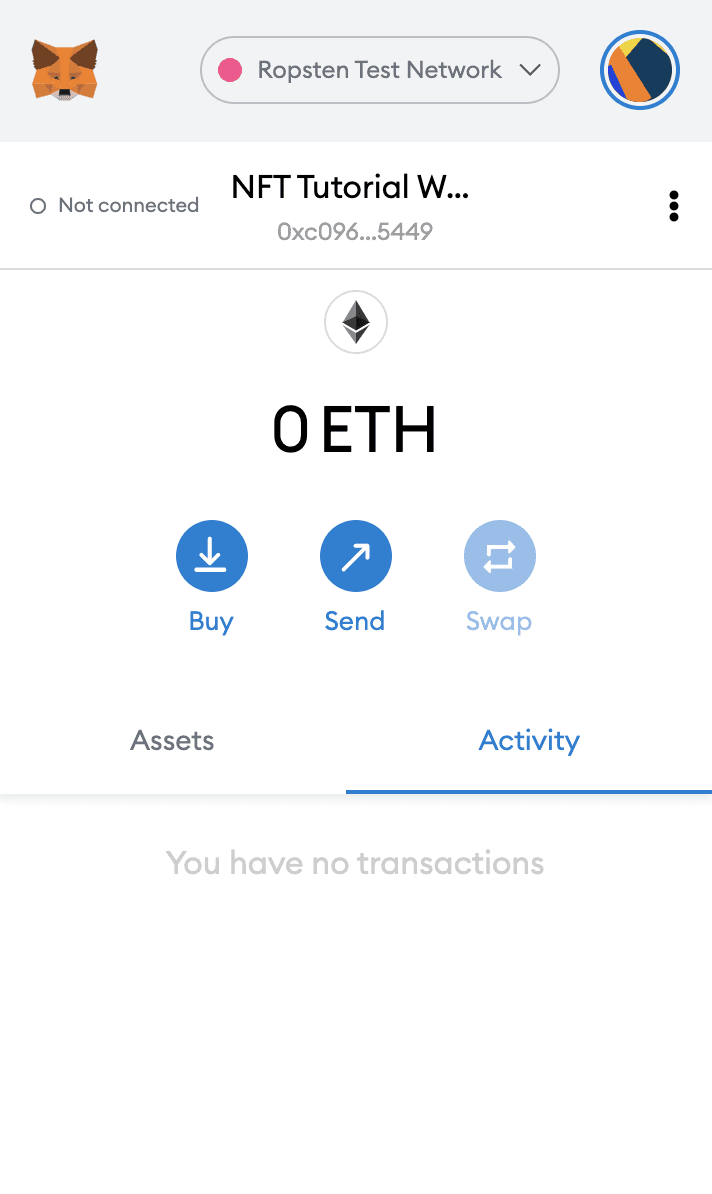
Step 4: Add ether from a Faucet
In order to deploy our smart contract to the test network, we’ll need some fake Eth. To get Eth you can go to the Ropsten faucet and enter your Ropsten account address, then click “Send Ropsten Eth.” You should see Eth in your Metamask account soon after!
Step 5: Check your Balance
To double check our balance is there, let’s make an eth_getBalance request using Alchemy’s composer tool. This will return the amount of Eth in our wallet. After you input your Metamask account address and click “Send Request”, you should see a response like this:
{"jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 0, "result": "0xde0b6b3a7640000"}
NOTE: This result is in wei not eth. Wei is used as the smallest denomination of ether. The conversion from wei to eth is: 1 eth = 10¹⁸ wei. So if we convert 0xde0b6b3a7640000 to decimal we get 1*10¹⁸ which equals 1 eth.
Phew! Our fake money is all there! 🤑
Step 6: Initialize our project
First, we’ll need to create a folder for our project. Navigate to your command line and type:
mkdir my-nft
cd my-nft
Now that we’re inside our project folder, we’ll use npm init to initialize the project. If you don’t already have npm installed, follow these instructions (we’ll also need Node.js, so download that too!).
npm init
It doesn’t really matter how you answer the installation questions, here is how we did it for reference:
package name: (my-nft)
version: (1.0.0)
description: My first NFT!
entry point: (index.js)
test command:
git repository:
keywords:
author:
license: (ISC)
About to write to /Users/thesuperb1/Desktop/my-nft/package.json:
{
"name": "my-nft",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "My first NFT!",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
Approve the package.json, and we’re good to go!
Step 7: Download Hardhat
Hardhat is a development environment to compile, deploy, test, and debug your Ethereum software. It helps developers when building smart contracts and dApps locally before deploying to the live chain.
Navigate to the terminal and make sure you're inside the my-nft project folder, then run:
npm install --save-dev hardhat
Check out this page for more details on installation instructions.
Step 8: Create Hardhat project
Inside our project folder run:
npx hardhat
You should then see a welcome message and option to select what you want to do. Select “create an empty hardhat.config.js”:
888 888 888 888 888
888 888 888 888 888
888 888 888 888 888
8888888888 8888b. 888d888 .d88888 88888b. 8888b. 888888
888 888 "88b 888P" d88" 888 888 "88b "88b 888
888 888 .d888888 888 888 888 888 888 .d888888 888
888 888 888 888 888 Y88b 888 888 888 888 888 Y88b.
888 888 "Y888888 888 "Y88888 888 888 "Y888888 "Y888
👷 Welcome to Hardhat v2.0.11 👷
? What do you want to do? …
Create a sample project
❯ Create an empty hardhat.config.js
Quit
This will generate a hardhat.config.js file for us which is where we’ll specify all of the set up for our project (on step 13).
Step 9: Add project folders
To keep our project organized, we’ll create two new folders. Navigate to the root directory of your project in your command line and type:
mkdir contracts
mkdir scripts
contracts/ is where we’ll keep our NFT smart contract code
scripts/ is where we’ll keep scripts to deploy and interact with our smart contract
Step 10: Write our contract
Now that our environment is set up, onto more exciting stuff: writing our smart contract code!
Open up the my-nft project in your favorite editor (we like VSCode). Smart contracts are written in a language called Solidity which is what we will use to write our MyNFT.sol smart contract.
1. Navigate to the “contracts” folder and create a new file called MyNFT.sol
2. Below is our NFT smart contract code, which is based off of the OpenZeppelin library's ERC721 implementation. Copy and paste the contents below into your MyNFT.sol file.
NOTE: If you want to attach a price to the NFT through the smart contract check out this tutorial.
//Contract based on https://docs.openzeppelin.com/contracts/3.x/erc721
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.7.3;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/ERC721.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Counters.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";
contract MyNFT is ERC721, Ownable {
using Counters for Counters.Counter;
Counters.Counter private _tokenIds;
constructor() public ERC721("MyNFT", "NFT") {}
function mintNFT(address recipient, string memory tokenURI)
public onlyOwner
returns (uint256)
{
_tokenIds.increment();
uint256 newItemId = _tokenIds.current();
_mint(recipient, newItemId);
_setTokenURI(newItemId, tokenURI);
return newItemId;
}
}
1. Because we are inheriting classes from the OpenZepplin contracts library, in your command line run the following to install the library into our folder:
textnpm install @openzeppelin/contracts@3.1.0-solc-0.7
So, what does this code do exactly? Let's break it down, line by line.
In lines 5-7, our code inherits three OpenZepplin smart contract classes:
- @openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/ERC721.solcontains the implementation of the ERC721 standard, which our NFT smart contract will inherit. (To be a valid NFT, your smart contract must implement all the methods of the ERC721 standard.) To learn more about the inherited ERC721 functions, check out the interface definition here.
- @openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Counters.solprovides counters that can only be incremented or decremented by one. Our smart contract uses a counter to keep track of the total number of NFTs minted and set the unique ID to our new NFT. Each NFT minted using a smart contract must be assigned a unique ID—here our unique ID is just determined by the total number of NFTs in existance. For example, the first NFT we mint with our smart contract has an ID of "1," our second NFT has an ID of "2," etc.
- @openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol sets up access control on our smart contract, so only the owner of the smart contract (you) can mint NFTs. Note, including access control is entirely a preference. If you'd like anyone to be able to mint an NFT using your smart contract, remove the word Ownable on line 10 and onlyOwner on line 17.
In Lines 10-28, we have our custom NFT smart contract, which is surprisingly short —it only contains a counter, a constructor, and single function! This is thanks to our inherited OpenZepplin contracts, which implement most of the methods we need to create an NFT, such as ownerOf (returns the owner of the NFT) and transferFrom(transfers ownership of the NFT).
On line 14, you'll notice we pass 2 strings, "MyNFT" and "NFT" into the ERC721 constructor. The first variable is the smart contract's name, and the second is its symbol. You can name each of these variables whatever you wish!
Finally, starting on line 16, we have our function mintNFT() that allows us to mint an NFT! You'll notice this function takes in two variables:
- address recipient specifies the address that will receive your freshly minted NFT
- string memory tokenURI is a string that should resolve to a JSON document that describes the NFT's metadata. An NFT's metadata is really what brings it to life, allowing it to have additional properties, such as a name, description, image, and other attributes. In part 2 of this tutorial, we will describe how to configure this metadata.
mintNFT calls some methods from the inherited ERC721 library, and ultimately returns a number that represents the ID of the freshly minted NFT.
Step 11: Connect Metamask & Alchemy to your project
Now that we've created a Metamask wallet, Alchemy account, and written our smart contract, it’s time to connect the three.
Every transaction sent from your virtual wallet requires a signature using your unique private key. To provide our program with this permission, we can safely store our private key (and Alchemy API key) in an environment file.
To learn more about sending transactions, check out this tutorial on sending transactions using web3.
First, install the dotenv package in your project directory:
npm install dotenv --save
Then, create a .env file in the root directory of our project, and add your Metamask private key and HTTP Alchemy API URL to it.
NOTE: Your .env file must be named .env ! Do not change the name to xx.env
- Follow these instructions to export your private key from Metamask
- See below to get HTTP Alchemy API URL and copy it to your clipboard
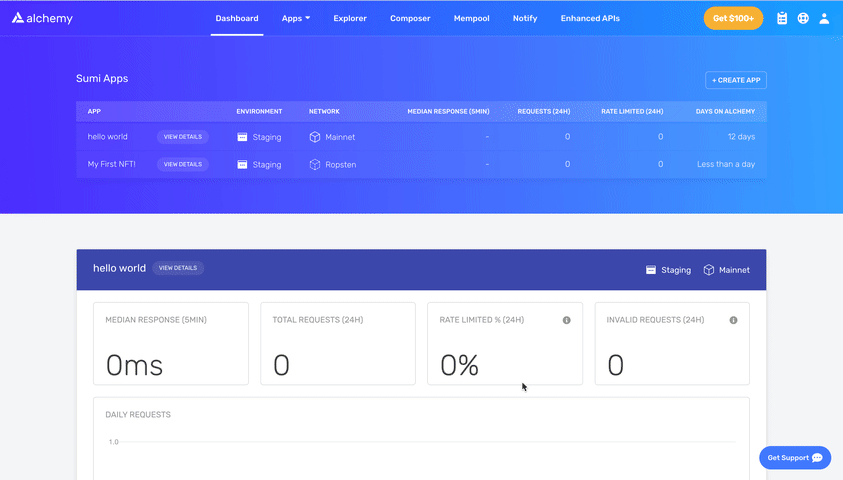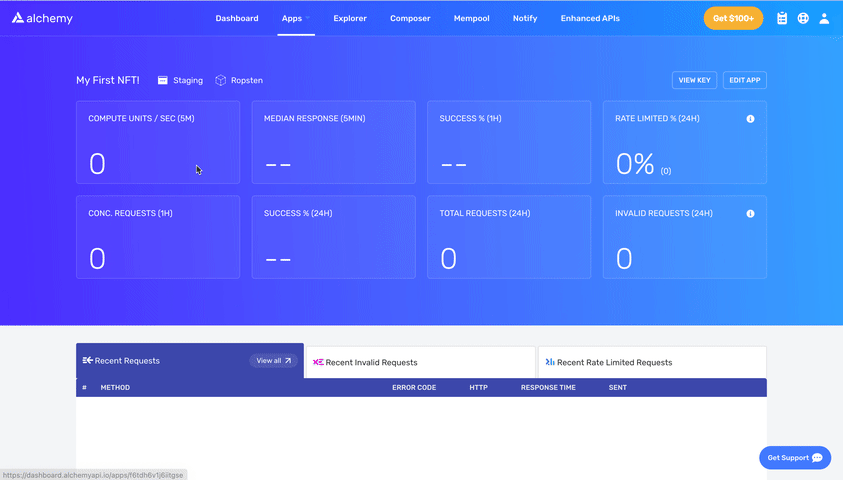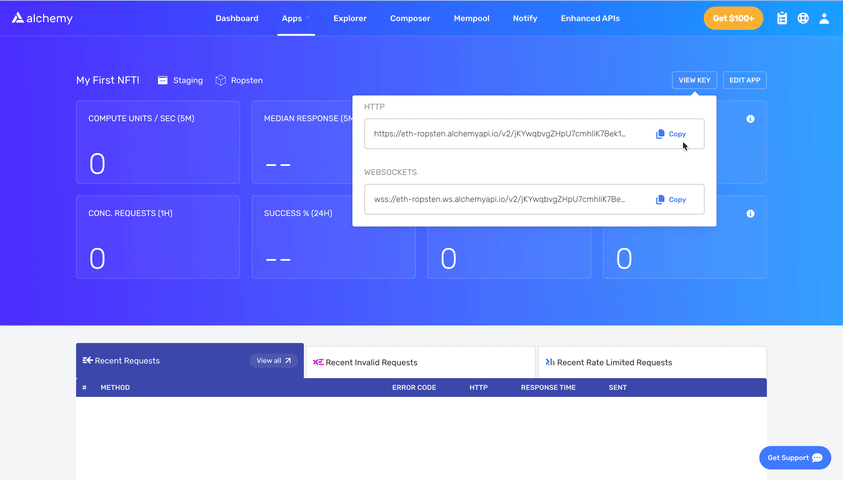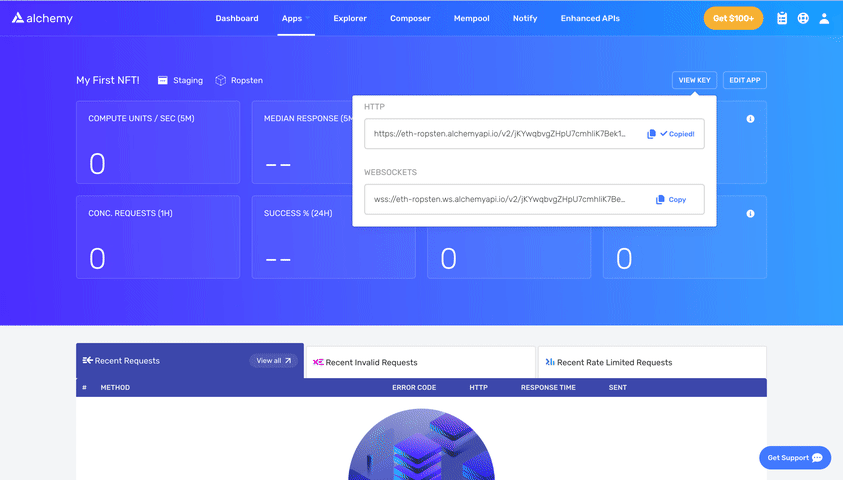
Your .env should look like this:
API_URL = "https://eth-ropsten.alchemyapi.io/v2/your-api-key"
PRIVATE_KEY = "your-metamask-private-key"
Step 12: Install Ethers.js
Ethers.js is a library that makes it easier to interact with and make requests to Ethereum by wrapping standard JSON-RPC methods with more user friendly methods.
Hardhat makes it super easy to integrate Plugins for additional tooling and extended functionality. We’ll be taking advantage of the Ethers plugin for contract deployment (Ethers.js has some super clean contract deployment methods).
In your project directory type:
npm install --save-dev @nomiclabs/hardhat-ethers "ethers@^5.0.0"
We’ll also require ethers in our hardhat.config.js in the next step.
Step 13: Update hardhat.config.js
We’ve added several dependencies and plugins so far, now we need to update hardhat.config.js so that our project knows about all of them.
Update your hardhat.config.js to look like this:
/**
* @type import('hardhat/config').HardhatUserConfig
*/
require('dotenv').config();
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-ethers");
const { API_URL, PRIVATE_KEY } = process.env;
module.exports = {
solidity: "0.7.3",
defaultNetwork: "ropsten",
networks: {
hardhat: {},
ropsten: {
url: API_URL,
accounts: [`0x${PRIVATE_KEY}`]
}
},
}
Step 14: Compile our contract
To make sure everything is working so far, let’s compile our contract. The compile task is one of the built-in hardhat tasks.
From the command line run:
npx hardhat compile
You might get a warning about SPDX license identifier not provided in source file , but no need to worry about that — hopefully everything else looks good! If not, you can always message in the Alchemy discord.
Step 15: Write our deploy script
Now that our contract is written and our configuration file is good to go, it’s time to write our contract deploy script.
Navigate to the scripts/ folder and create a new file called deploy.js, adding the following contents to it:
async function main() {
// Grab the contract factory
const MyNFT = await ethers.getContractFactory("MyNFT");
// Start deployment, returning a promise that resolves to a contract object
const myNFT = await MyNFT.deploy(); // Instance of the contract
console.log("Contract deployed to address:", myNFT.address);
}
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
Hardhat does an amazing job of explaining what each of these lines of code does in their Contracts tutorial, we’ve adopted their explanations here.
const MyNFT = await ethers.getContractFactory("MyNFT");
A ContractFactory in ethers.js is an abstraction used to deploy new smart contracts, so MyNFT here is a factory for instances of our NFT contract. When using the hardhat-ethers plugin ContractFactory and Contract instances are connected to the first signer by default.
const myNFT = await MyNFT.deploy();
Calling deploy() on a ContractFactory will start the deployment, and return a Promise that resolves to a Contract. This is the object that has a method for each of our smart contract functions.
Step 16: Deploy our contract
We’re finally ready to deploy our smart contract! Navigate back to the root of your project directory, and in the command line run:
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network ropsten
You should then see something like:
Contract deployed to address: 0x81c587EB0fE773404c42c1d2666b5f557C470eED
If we go to the Ropsten etherscan and search for our contract address we should be able to see that it has been deployed successfully. The transaction will look something like this:
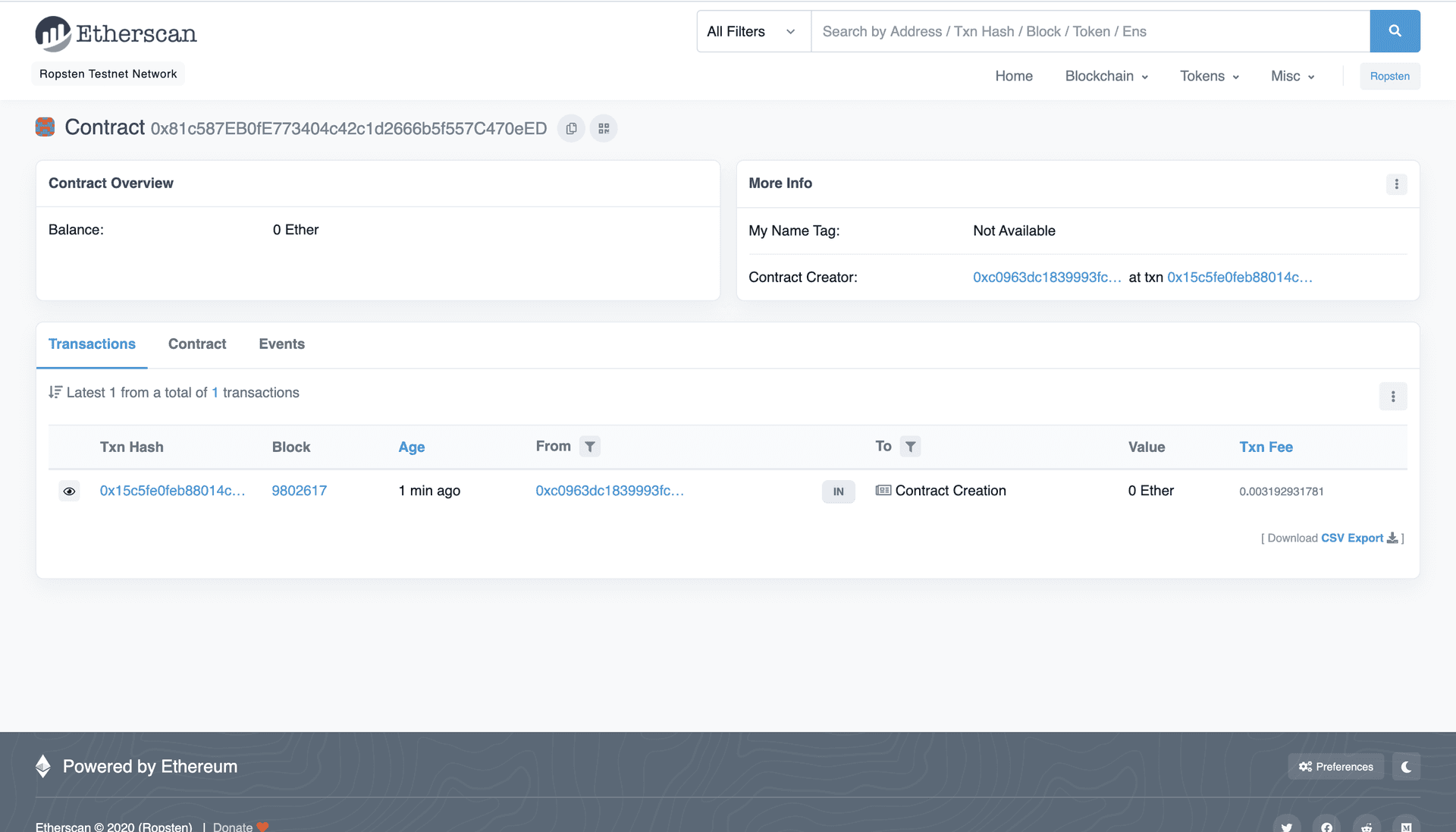
The From address should match your Metamask account address and the To address will say “Contract Creation.” If we click into the transaction, we’ll see our contract address in the To field:
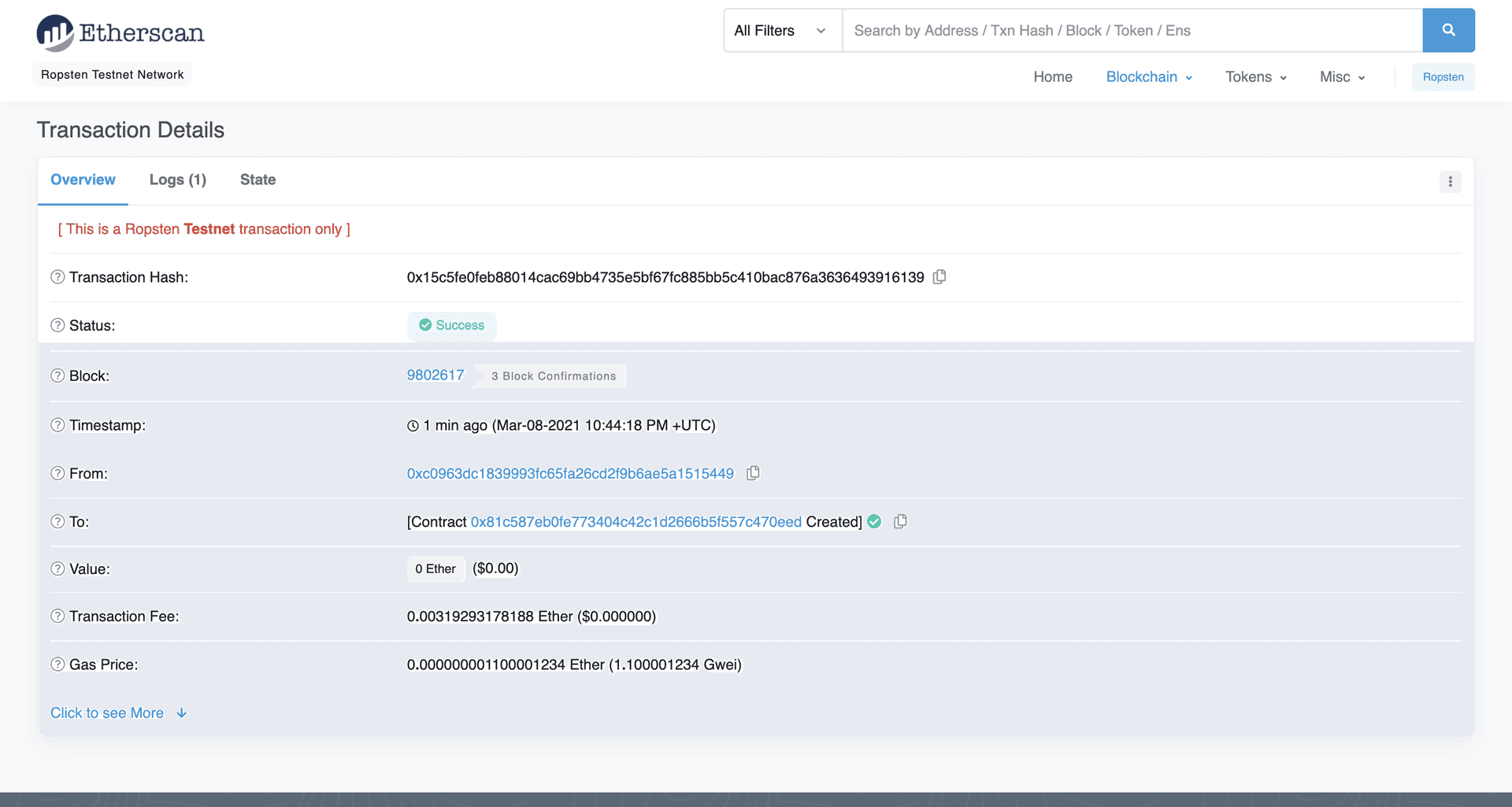
To understand what’s going on under the hood, let’s navigate to the Explorer tab in our Alchemy dashboard . If you have multiple Alchemy apps make sure to filter by app and select “MyNFT”.
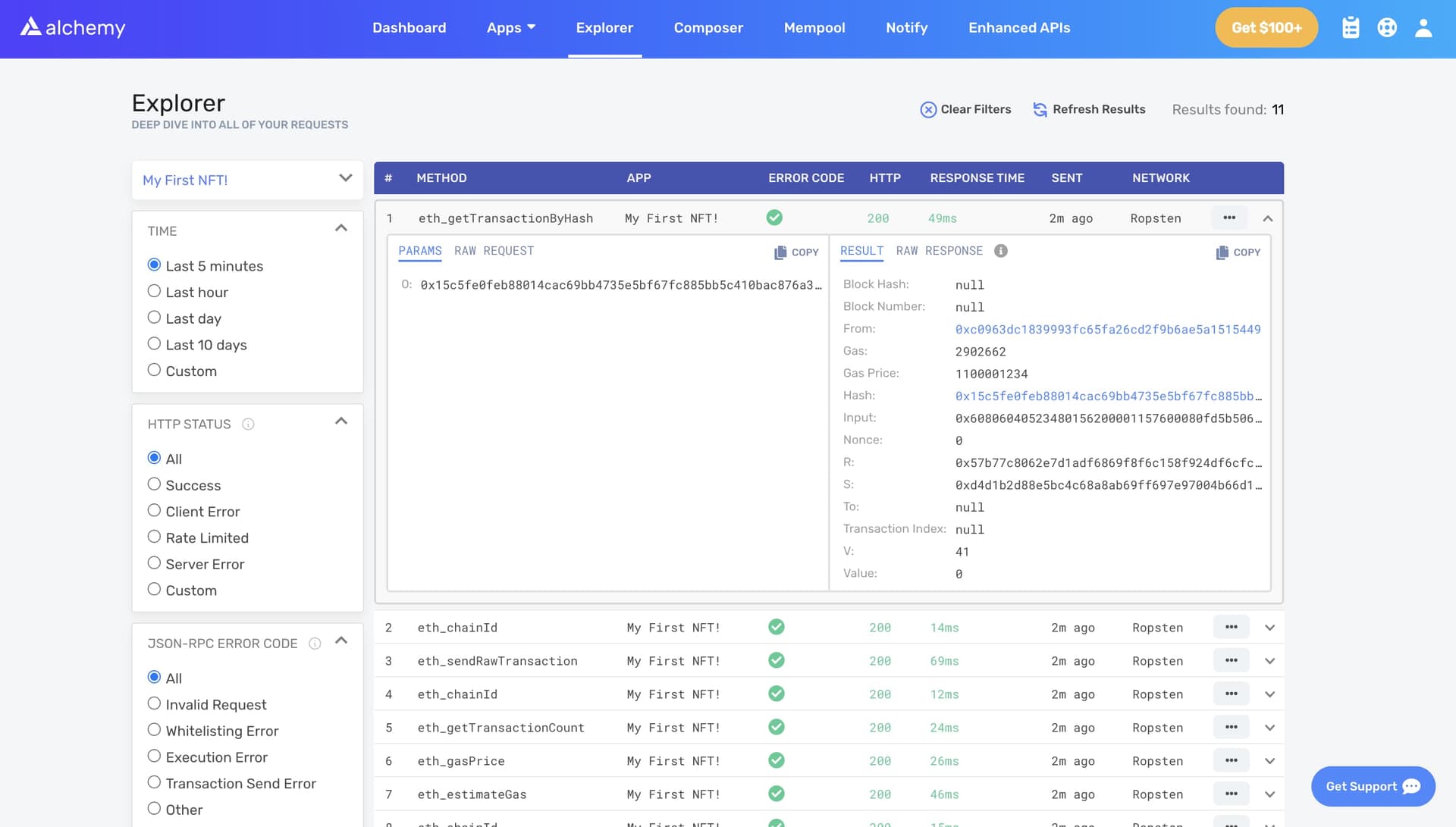
Here you’ll see a handful of JSON-RPC calls that Hardhat/Ethers made under the hood for us when we called the .deploy() function.
Two important ones to call out here are eth_sendRawTransaction, which is the request to actually write our smart contract onto the Ropsten chain, and eth_getTransactionByHash which is a request to read information about our transaction given the hash (a typical pattern when sending transactions).
To learn more about sending transactions, check out this tutorial on sending transactions using Web3.
That’s all for Part I of this tutorial. In Part II, we’ll actually interact with our smart contract by minting an NFT, and in Part III we'll explain how to view your NFT in Metamask! 🤑
Alchemy Newsletter
Be the first to know about releases
Sign up for our newsletter
Get the latest product updates and resources from Alchemy
By entering your email address, you agree to receive our marketing communications and product updates. You acknowledge that Alchemy processes the information we receive in accordance with our Privacy Notice. You can unsubscribe anytime.
Related articles

How to Build a Stablecoin in 2026
A technical guide covering everything you need to know to build your own stablecoin.

How to Build Solana AI Agents in 2026
A technical tutorial showing you how to build agents on Solana.

How to Make a Memecoin on Solana: A Step-by-Step Guide
Learn how to make a memecoin on Solana from a launchpad or DIY.